Two forms of an amino acid, related by proton transfer Does one of these forms dominate the equilibrium?The acid dissociation constant for the guanidinium group in arginine has historically been posited as 125, but there is substantial variation in published values over the years8 Water pKldehyde pKa = 11 Alpha proton of ester pKa = 25 12 Terminal alkyne pKa = 25 13 Amine pKa = 38‐40 14 Aromatic Aryl 43, benzylic 41 15 Alkene vinyl 45‐50;

Exceptionally Versatile Arginine In Bacterial Post Translational Protein Modifications
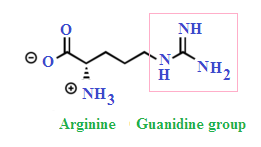
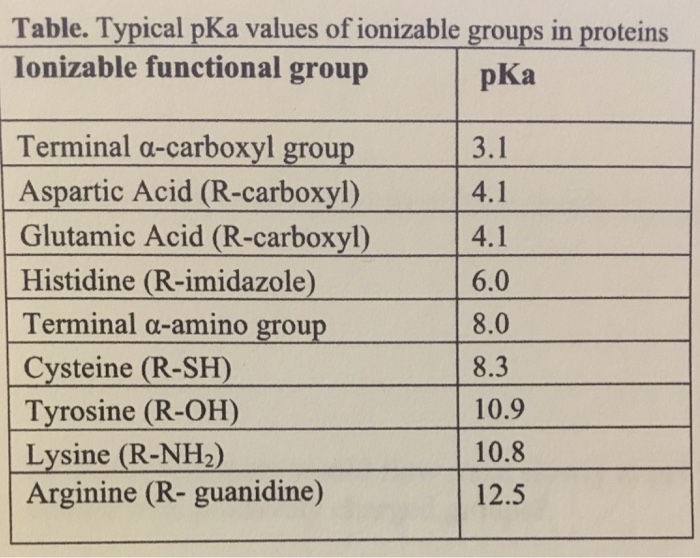
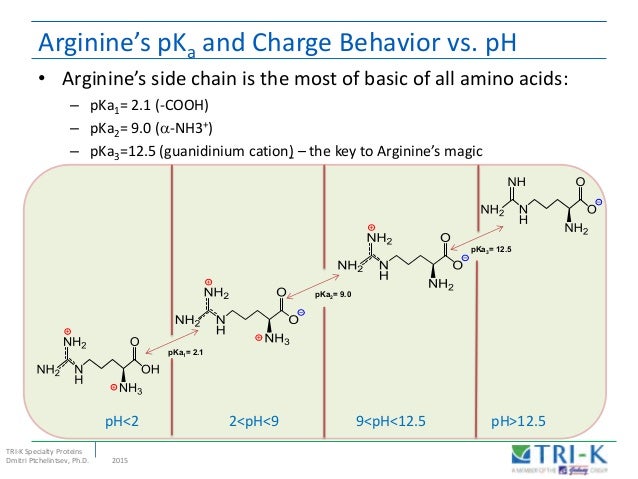
Pka of guanidine group of arginine
Pka of guanidine group of arginine-The amino acid sidechain of arginine consists of a 3carbon aliphatic straight chain, the distal end of which is capped by a guanidinium group, which has a p Ka of 1248, and is therefore always protonated and positively charged at physiological pHMar 22, 15 · However, the accepted pK a values of 136 and 134 for the conjugate acids of guanidine and N‐methyl guanidine, respectively, 23, 24 suggest strongly that the intrinsic pK a of the arginine side chain is significantly higher than 12 If so, then even when buried in the driest and most hydrophobic environments available, it may not become



Classification Of Amino Acids Video Khan Academy
Oct 26, 17 · Carbenes, Amino Carboxylic Acids (OH) Cyclopentadiene Dithianes Esters Ethers Fluorenes Germanes (GeH) Guanidine (NH) Halides Heteroaromatics HornerWadsworth Emmons Reag Hydantoin Hydrazine, Hydrazone Hydrazoic Acid Hydrogen cyanide Hydrohalic acids Hydrocarbons Hydroxylamines, Hydroxamic AcidsDec 17, 1996 · Guanidine Derivatives Rescue the Arg418Ala Mutation of Tritrichomonas foetus IMP Dehydrogenase† Biochemistry 05, 44 (50) , DOI /biw Brian C Tripp,, Chingkuang Tu, and, James G Ferry Role of Arginine 59 inFor a comparative series that includes guanidine and alkylguanidines, substituent size is inversely related to kcat Brønsted analysis of guanidines with varying pKa values indicates that a partial positive charge is implicated in rescue, consistent with the proposed role of arginine 57 in catalysis
Chloride, Guanidinium Chloride, Guanidium Guanidine Guanidine Hydrochloride Guanidine Monohydrate Guanidine Monohydrobromide Guanidine MonohydrochlorideGroup A Nonpolar amino acids Aliphatic cyclic structure and the Nitrogen is bonded to two carbon toms (secondary amine) → proline is an imino acid Aliphatic hydrocarbon Fig 33a1, p60 Sulfur containing Aromatic (indol ring) Aromatic (benzene ring) Fig 33b1, p60 Amino Acids (cont'd) • Group B Neutral Polar side chains Ser, ThrOct 02, 14 · The guanidine side chain group of the residue Arg18 of the peptide substrates (the residue at position 3 from the phosphorylated serine) has stable HB interactions with the side chain carboxylate group of the PKA residue Glu127, with the backbone CO of the residue Thr51 in the glycinerich loop of the PKA small lobe, and with the hydroxyl at
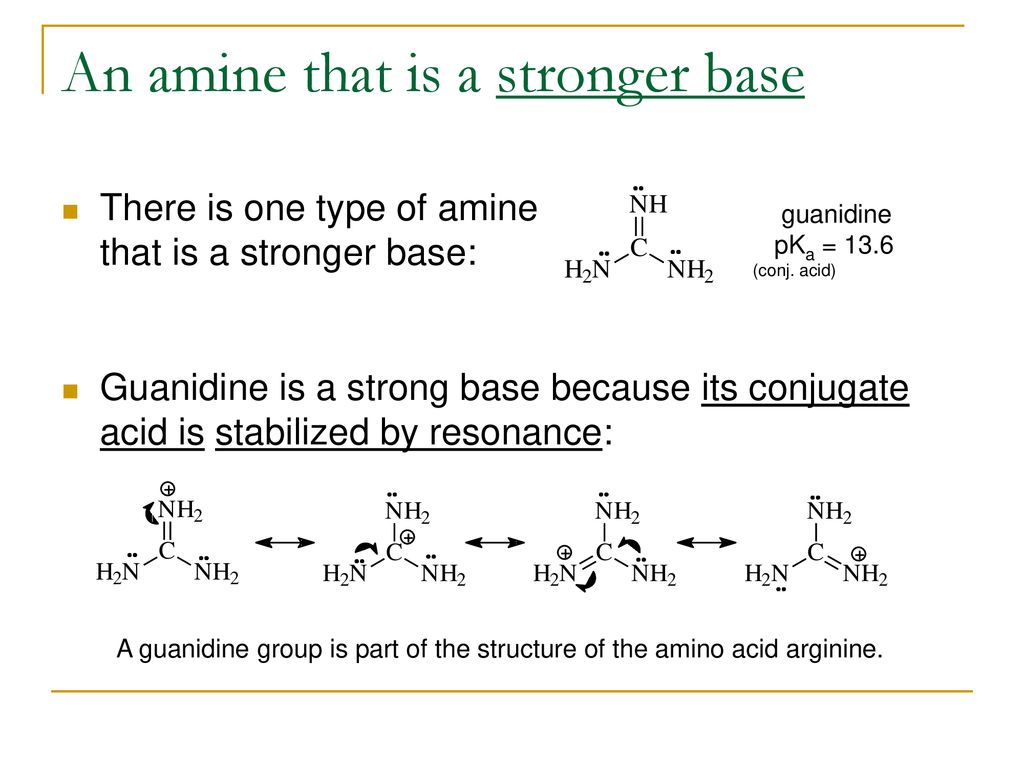
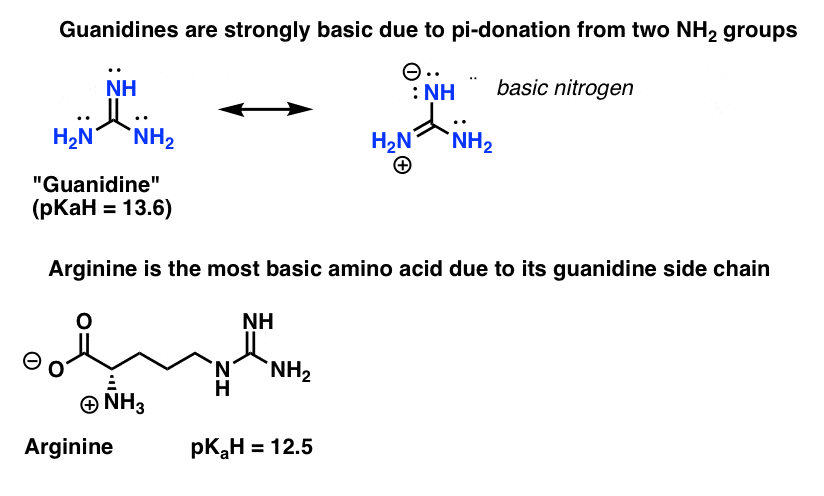
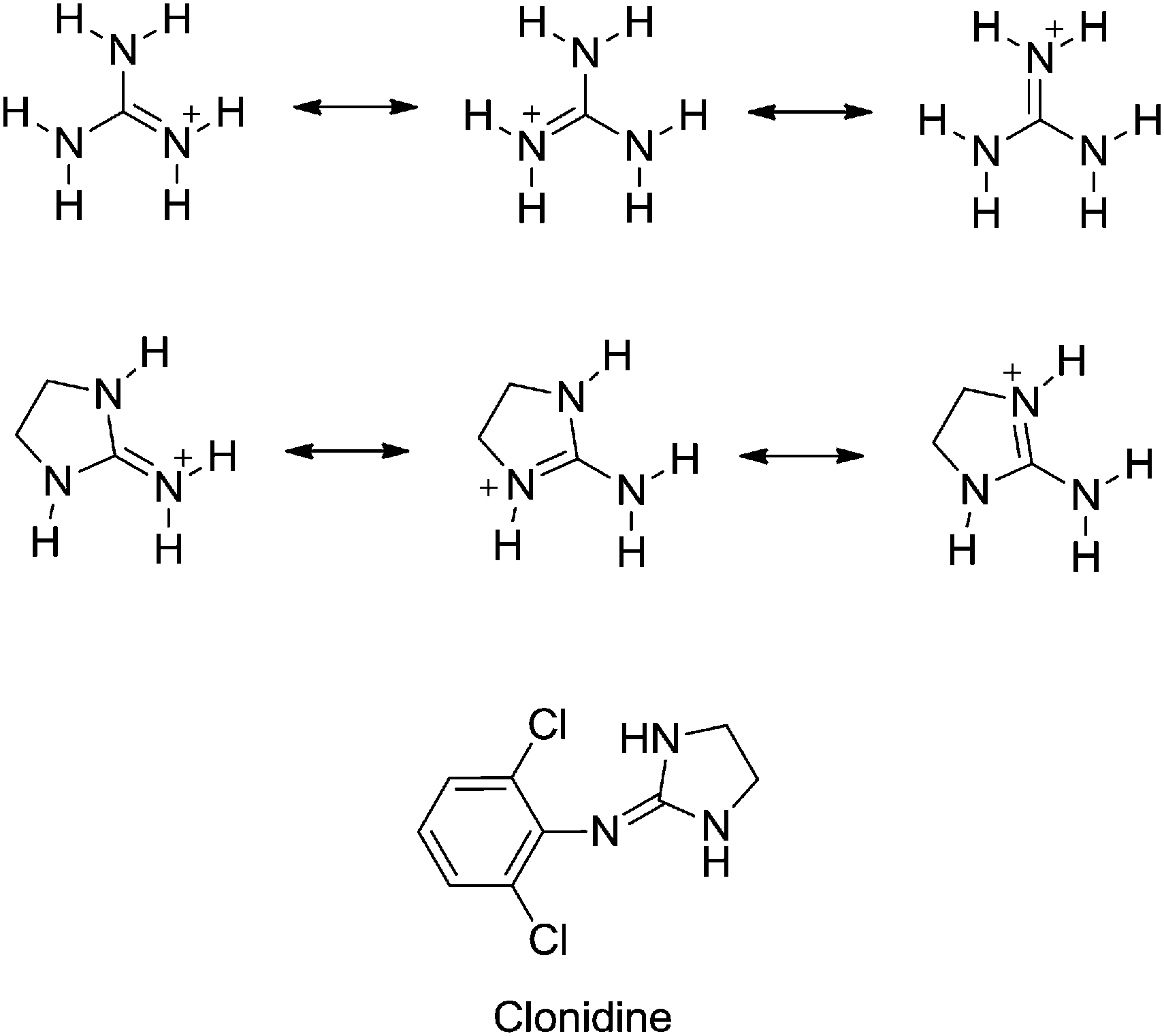
Guanidine, an organic compound of formula HN=C(NH 2) 2It was first prepared by Adolph Strecker in 1861 from guanine, which had been obtained from guano, and this is the origin of the nameThe compound has been detected in small amounts in a variety of plant and animal products, but some of its derivatives are widely distributed and are of considerable importance, especially in theIn the wild type (in 150 mM salt) the pKa of this group decreases from approximately 95 in the unphotolyzed pigment to approximately 58 in the M intermediate, leading to early proton release at neutral pHGuanidino compounds can be synthesized by transamidination reactions using arginine as a guanidine group donor The efficiency of guanidino biosynthesis is often affected by the supply of arginine and the inhibition of the coproduct ornithine To alleviate this shortcoming, we designed a



Selective Labelling Of Arginine Residues Engaged In Binding Sulfatedglycosaminoglycans Biorxiv


Amino Acids Chemistry Biochemistry Nutrition Amit Kessel Ph D
Arginine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged guanidino group Arginine is well designed to bind the phosphate anion, and is often found in the active centers of proteins that bind phosphorylated substrates As a cation, arginine, as well as lysine, plays a role in maintaining the overall charge balance of a proteinGuanine (/ ˈ ɡ w ɑː n ɪ n /;Lysine an essential amino acid, has a positively charged εamino group (a primary amine) Lysine is basically alanine with a propylamine substituent on theβcarbon The εamino group has a significantly higher pK a (about 105 in polypeptides) than does the αamino group The amino group is highly reactive and often participates in a reactions at the active centers of enzymes



Chem 365 Chapter 4 Flashcards Quizlet



Arginine Residues At Internal Positions In A Protein Are Always Charged Pnas
Feb 27, 16 · The important side chain nucleophiles (in order from most to least nucleophilic) are Cys (RSH, pKa 8595), His (pKa 67), Lys (pKa 105) and Ser (ROH, pKa 13) An understanding of the chemical reactivity of the various R group side chains of the amino acids in a protein is important since chemical reagents that react specifically with a givenThe pKa of guanidine is 125(1) This value indicates that guanidine will exist almost entirely as a cation at environmental pH (pH 59) Volatilization from moist soil and water surfaces is not an important environmental fate process since cations do not volatilize(SRC) The potential to volatilize from dry soil surfaces exists based upon an estimated vapor pressure of 22 mm Hg(SRC),Compare the pKa's The pKa of the acid is near 5, and the pKa of the ammonium is near 9 The ammonium holds the proton more tightly than does the acid The proton stays on the nitrogen Amino acids are zwitterionic



Arginine Mass Shift 156 Da Peptide Chemistry Portal


Amino Acid Titration Lecture Notes 1 Studocu
Arginine regulates the pKa of the group responsible for the lightdriven proton release in bacteriorhodopsin Guanidine Hydrochloride Restores It By Sergei Balashov, Rosalie Crouch, Saurav Misra, Rajni Govindjee, and Don Menick Mutation of Arginine 134 to Lysine Alters the pK a s of Key Groups Involved in Proton Pumping byIn this study, the compounds Nmethylguanidine and Nethylguanidine were used to model the charged and all neutral protonation states of the arginine side chain The relative stabilities of all five neutral tautomers were investigated systematically forGlycocyamine (or guanidinoacetate) is a metabolite of glycine in which the amino group has been converted into a guanidine by guanylation (transfer of a guanidine group from arginine)In vertebrate organism it is then transformed into creatine by methylation Glycocyamine is used as a supplement and as a feed additive in poultry farmingHowever, the metabolism of creatine from



Structural Insight Into Arginine Degradation By Arginine Deiminase An Antibacterial And Parasite Drug Target Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Histidine Side Chain Pka Page 5 Line 17qq Com
Chromatography in the presence of 6M guanidine hydrochloride yields only a peak for a protein of 60 kDa Chromatography in the presence of 6M guanidine hydrochloride and 10mM bmercaptoethanol yields peaks for proteins of 34 kDa and 26 kDa Explain what can be determined about the structure of this protein from these data and whyA value) of the arginine guanidinium group is This is substantially higher than that of ~12 often used in structurebased electrostatics calculations and cited in biochemistry textbooks The revised intrinsic pK a value helps explains why arginine side chains in proteins are always predominantly charged, even at pH values as great as 10Mar 12, 1997 · Stereochemistry of guanidinemetal interactions Implications for Largininemetal interactions in protein structure and function Proteins Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics 06 , 65 (/protv653) ,



Of Amino Acids Titration Curves Titration Of Amino Acids Titration Of Glycine Titration Of Arginine Ppt Download



Table 1 From A 13c Detected 15n Double Quantum Nmr Experiment To Probe Arginine Side Chain Guanidinium 15nh Chemical Shifts Semantic Scholar
A new variant of the solid phase synthesis of argininecontaining peptides was proposed The conditions for the attachment to the Wang polymer of N alphaFmocarginine containing a protonated guanidine group were found We demonstrated that this attachment is accompanied by neither racemization nor the attachment of the second Arg residue4 4D There are amino acids possible in each of the four positions × × × = 5 a Serotonin lacks the carboxyl group of tryptophan (It also contains a hydroxyl group, but this should have minimal effect on the amino group's pKa because it's so far away) bAlanine is a hydrophobic molecule It is ambivalent, meaning that it can be inside or outside of the protein moleculeThe α carbon of alanine is optically active;


Amino Acids And Proteins


Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Basicity Of Guanidine
Amino acids Classification PROBLEM 1 Explain why when the imidazole ring of histidine is protonated, the doublebonded nitrogen is the nitrogen atom that accepts the proton same for guanidine group in arginine CO2H NH2 H N N CO2H NH2 N H H2N NHNet charge at low pH = 3, so have to add 3 equivalents of base to get to net charge zero 3 equiv base would completely titrate the αcarboxyl, Rcarboxyl, and His imidazole, so pI would be halfway between pK of imidazole and pK of αamino group, ie (60Feb 22, 16 · Lysine and arginine are the two positively charged amino acids in proteins that have high aqueous pKa's (~105 for Lys 1 and ~138 for Arg 2) indicating a


More Biologically Active Amines Ppt Download



Role Of Guanidinium Group In The Insertion Of L Arginine In Dmpe And Dmpc Lipid Interphases Sciencedirect
Arginine residues are key to initiate these aberrant interactions Crucial for scavenging is the guanidinium group of its side chain, not its charge, indicating a key role of πstacking chemistry for driving aberrant fibril interactionsThe minor structural modificationsthe type of the guanidine group (pyrrole guanidine (GCP) and arginine) and the linker length (presence or absence of glycine)greatly affected the conformation of compounds and consequently the binding to double (ds) and singlestranded (ss) polynucleotides GCP peptide with shorter linker was able toArginine C6H14N4O2 CID 6322 structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety


Exam 3 Answer Key



Electrochemical Structures For Various L Arginine Analogues And Organic Download Scientific Diagram
However, the accepted pK a values of 136 and 134 for the conjugate acids of guanidine and Nmethyl guanidine, respectively, 23, 24 suggest strongly that the intrinsic pK a of the arginine side chain is significantly higher than 12 If so, then even when buried in the driest and most hydrophobic environments available, it may not becomeFeb 13, 19 · It is demonstrated that NMR spectroscopy is a powerful technique for separating and measuring each distinct pKa value of the amino groups located around aminoglycoside antibiotics Unambiguous assignments were made for each individual amine and guanidine substituent on 2deoxystreptamine, neamine, neomycin C, paromomycin, tobramycin, kanamycinWhen blocking guanidine groups of arginine residues of Na, KATPase and glutamate dehydrogenase the inhibiting action of cholesterol was absent The obtained data evidence for the possibility of a direct interaction of cholesterol with membrane enzymes as well as for the important significance of guanidine groups of arginine residues of
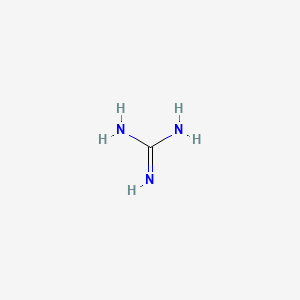


Guanidine Ch5n3 Pubchem


Kevin Ahern S Biochemistry 450 550 At Oregon State University
Jul 01, 1978 · Background The guanidine group defines chemical and physicochemical properties of many compounds of medical interest and guanidinecontaining derivatives constitute a very important class of therapeutic agents suitable for the treatment of a wide spectrum of diseases Objective To review the most important pharmacological properties, mechanisms of action andThe pK a values of seven novel guanidine derivatives, six of them possessing heteroalkyl substituents capable of forming intramolecular hydrogen bonds, were determined in acetonitrile (MeCN) by using the UV/Vis spectrophotometric titration method The obtained pK a values range from 247 to 272 The most basic among the studied guanidines was found to be by ca 4 pK aAmino Acids Proteins are polymers of amino acidsAn amino acid is a carbon atom (called the a carbon) bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amine group, a carboxylic acid group, and one of different side chains The structure of an amino acid is shown at right (R is a generic letter used to take the place of the side chain)



Selective Labelling Of Arginine Residues Engaged In Binding Sulfatedglycosaminoglycans Biorxiv


1 4 1 Acid Base Chemistry Of Amino Acids Chemistry Libretexts
Such concern arises from the facts that arginine decreases melting temperature and perturbs the spectroscopic properties of certain proteins and contains a guanidinium group, which is a critical chemical structure for denaturing activity of guanidine hydrochlorideThe binding affinity of llysine, larginine (substrate), and NomegaOHlarginine (type 2 binders) increases inversely with the pKa of the side chain Binding of llysine is more than 10 times weaker, and the substrate Michaelis constant (Km) is >6fold greater (weaker binding) in the His141Asn mutant than in wildtype arginaseAllylic 43 16 Alkane pKa = above 50
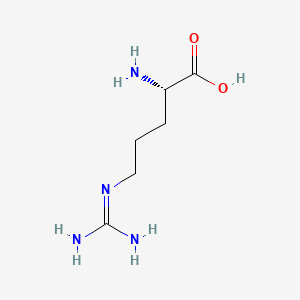


Arginine C6h14n4o2 Pubchem



Amino Acid Standard Amino Acids Britannica
The pKa for the conjugate acid of the amide (in which the amide N is protonated and has a plus charge) is much lower, around 05, than the pKa for the conjugate acid of an amine At 2 pH units greater than its pKa, the charged amide N is close to 100% deprotonated The pka of the protonated group is important since the rate of H exchange isIn proteins, only the Lisomer is found Note that alanine is the αamino acid analog of the αketo acid pyruvate, anDec 23, 11 · In order to enhance the potential for specificity and affinity in arginine‐mediated molecular recognition, we have developed an approach to the synthesis of peptides that incorporates an α‐guanidino acid as a novel arginine mimetic α‐Guanidino acids, derived from α‐amino acids, with guanidinylation of the amino group, were


Dietary Arginine Metabolic Environmental Immunological And Physiological Interrelationships World S Poultry Science Journal Cambridge Core



Tetrazole Binding To Amidine Bases
Aminoguanidine is a onecarbon compound whose unique structure renders it capable of acting as a derivative of hydrazine, guanidine or formamide It has a role as an EC 1434 (monoamine oxidase) inhibitor and an EC (nitric oxide synthase) inhibitor It is a member of guanidines and a onecarbon compoundOr G, Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA) In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosineThe guanine nucleoside is called guanosine With the formula C 5 H 5 N 5 O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidineimidazole ring systemGuanidine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt form of guanidine, a strong basic compound with parasympathomimetic activityGuanidine hydrochloride enhances the release of acetylcholine following a nerve impulse and potentiates acetylcholine actions on muscarinic and nicotinic receptors It also appears to slow the rates of depolarization and repolarization of muscle cell


Figure S1 Ionization Of Arginine Methyl Ester In Water A Pka Nh 3 Download Scientific Diagram



Solved Creatine And Arginine Are Two Amino Acids Containi Chegg Com



Biochemistry Amino Acids Flashcards Quizlet



Side Chain Protonation States Of A Fluorescent Arginine The Journal Of Organic Chemistry X Mol



Arginine Wikipedia


Review Of Acid Base Chemistry



Basic And Acidic Amino Acids Youtube


Solved A The Polypeptide Dfevdergyqticmknys Is Subjecte Chegg Com



Exceptionally Versatile Arginine In Bacterial Post Translational Protein Modifications



Arginine Its Pka Value Revisited Abstract Europe Pmc



Role Of Guanidinium Group In The Insertion Of L Arginine In Dmpe And Dmpc Lipid Interphases Sciencedirect



Why Isn T The Side Chain Of Arginine Totally Protonated At Low Ph Chemistry Stack Exchange


Proteins In Cosmetics Science Technolopgy Applications



A Cation P Interaction In A Transmembrane Helix Of Vacuolar Atpase Retains The Proton Transporting Arginine In A Hydrophobic Environment Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Large Shifts In Pka Values Of Lysine Residues Buried Inside A Protein Pnas


5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry


Chemical Structure Of Three Amino Acids With Guanidinium Group Download Scientific Diagram


Substituent Effects On The Basicity P K A Of Aryl Guanidines And 2 Arylimino Imidazolidines Correlations Of Ph Metric And Uv Metric Values With P New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C7nje
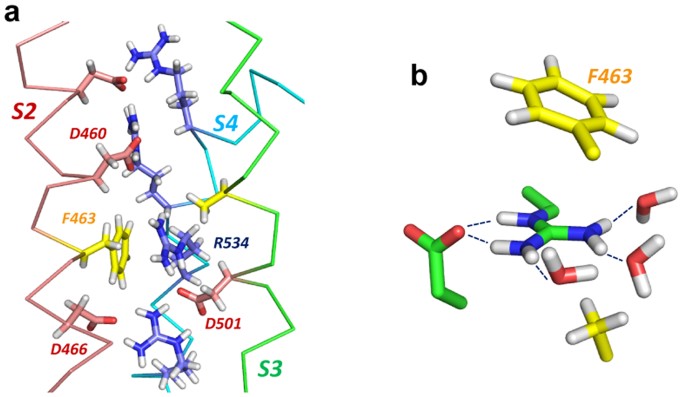


Arginine Side Chain Interactions And The Role Of Arginine As A Gating Charge Carrier In Voltage Sensitive Ion Channels Scientific Reports


Deprotonation Reaction Of Arginine In The Gas Phase R Means The Download Scientific Diagram



I M In Biochem 1 And We Re Now Learning The Amino Acids Learning About Pka And Ionization Of Side Chains At Certain Phs It S Been Too Long Since I Ve Taken Gen Chem What



Classification Of Amino Acids Video Khan Academy



Selective Labelling Of Arginine Residues Engaged In Binding Sulfatedglycosaminoglycans Biorxiv



Classical Guanidine Synthesis Guanidine Core Structure Obtained By Download Scientific Diagram
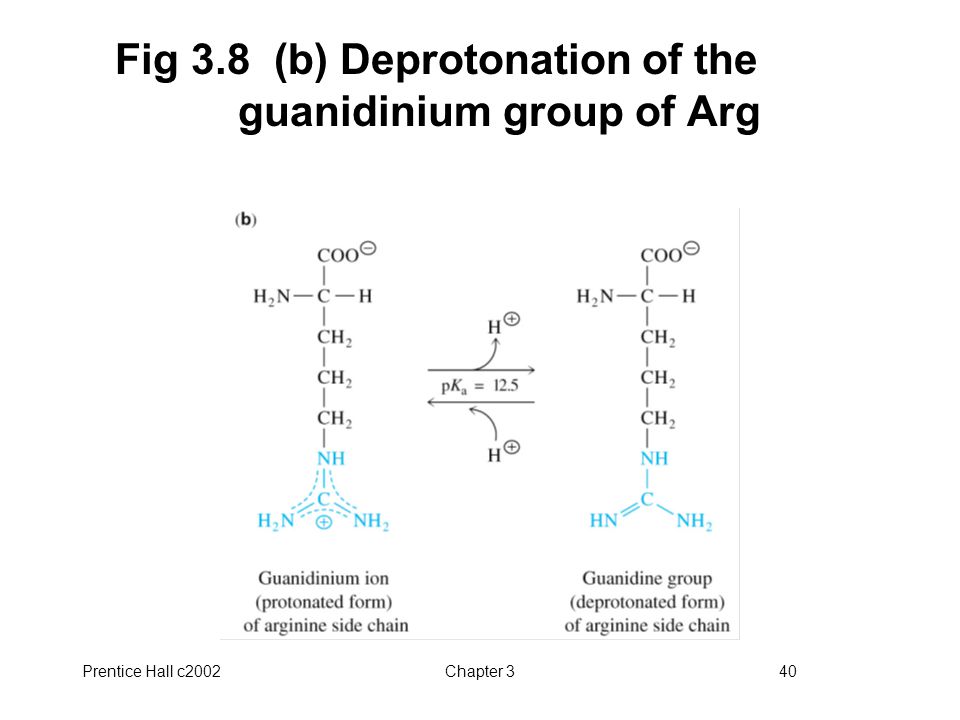


Principles Of Biochemistry Ppt Video Online Download



Exceptionally Versatile Arginine In Bacterial Post Translational Protein Modifications



Arginine Its Pka Value Revisited Fitch 15 Protein Science Wiley Online Library



Amino Acids Flashcards Quizlet
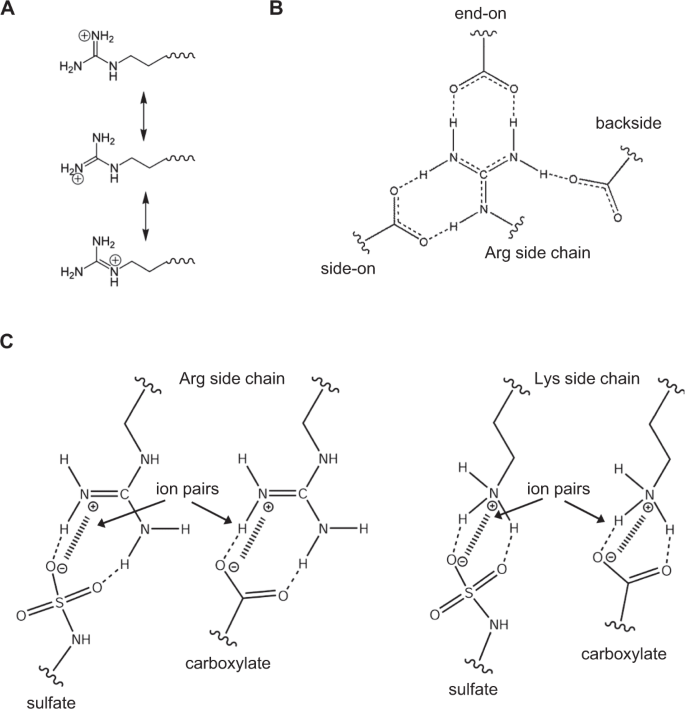


Lysines And Arginines Play Non Redundant Roles In Mediating Chemokine Glycosaminoglycan Interactions Scientific Reports
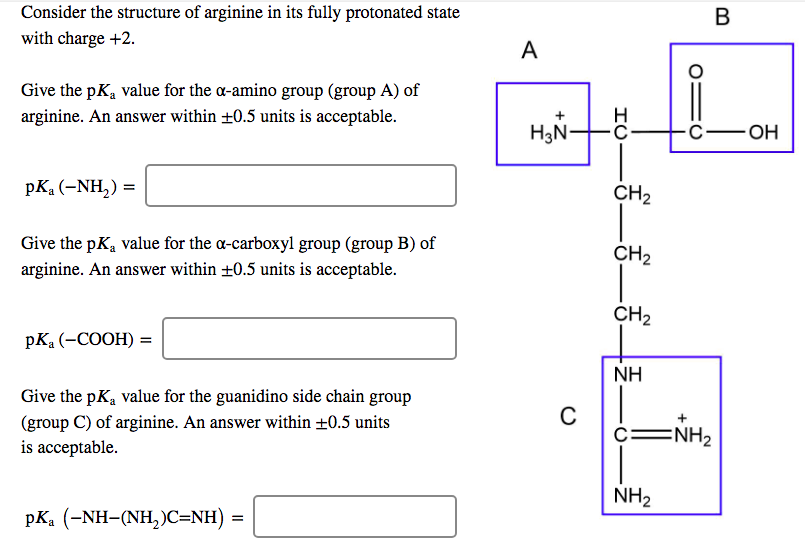


Solved Consider The Structure Of Arginine In Its Fully Pr Chegg Com



Phosphate Guanidine Interaction Based Fluorometric Strategy For Protein Kinase Activity Sensing Sciencedirect


The Arginine Sensing And Transport Binding Sites Are Distinct In The Human Pathogen Leishmania



Exceptionally Versatile Arginine In Bacterial Post Translational Protein Modifications



The Structure Of Non Ionized Arg Molecule A And Ionized Arg B Download Scientific Diagram



Protein Ionizable Groups Pk Values And Their Contribution To Protein Stability And Solubility Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Effect Of Methylation On The Side Chain Pka Value Of Arginine Evich 16 Protein Science Wiley Online Library



How Can The Isoelectric Point Of Arginine Be Determined Quora
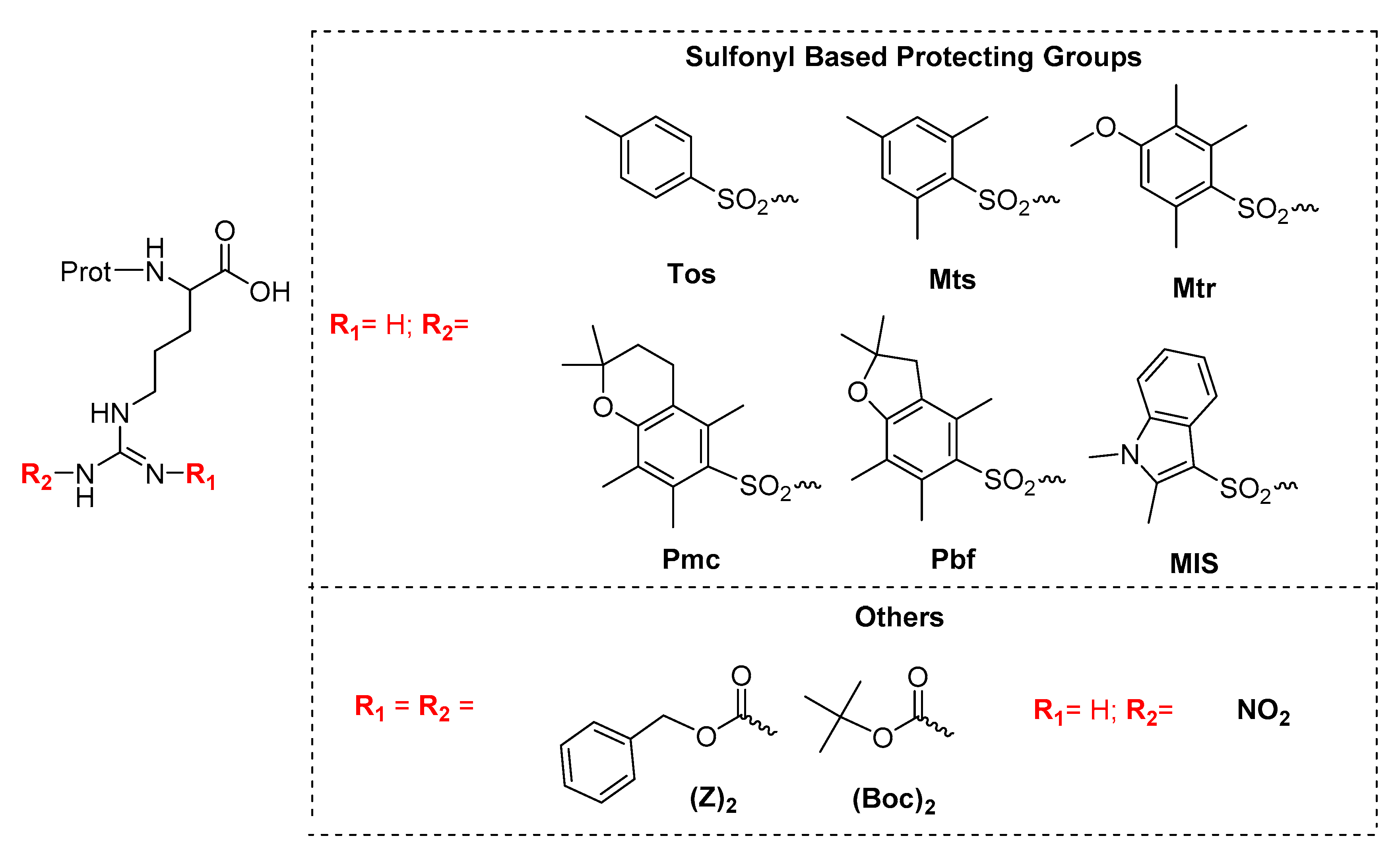


Ijms Free Full Text Revisiting No2 As Protecting Group Of Arginine In Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis Html


Kevin Ahern S Biochemistry 450 550 At Oregon State University
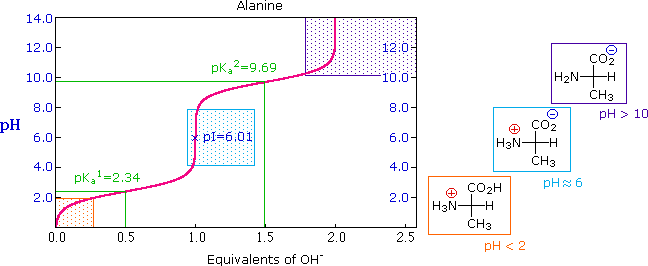


26 3 Amino Acids The Henderson Hasselbalch Equation And Isoelectric Points Chemistry Libretexts



Solved Creatine And Arginine Are Two Amino Acids Containi Chegg Com



Arginine Resonance Page 1 Line 17qq Com


V



Dna Rna Recognition Controlled By The Glycine Linker And The Guanidine Moiety Of Phenanthridine Peptides Sciencedirect
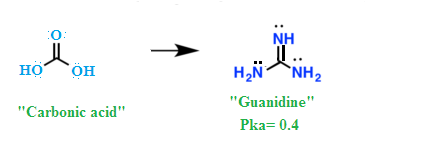


Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Basicity Of Guanidine
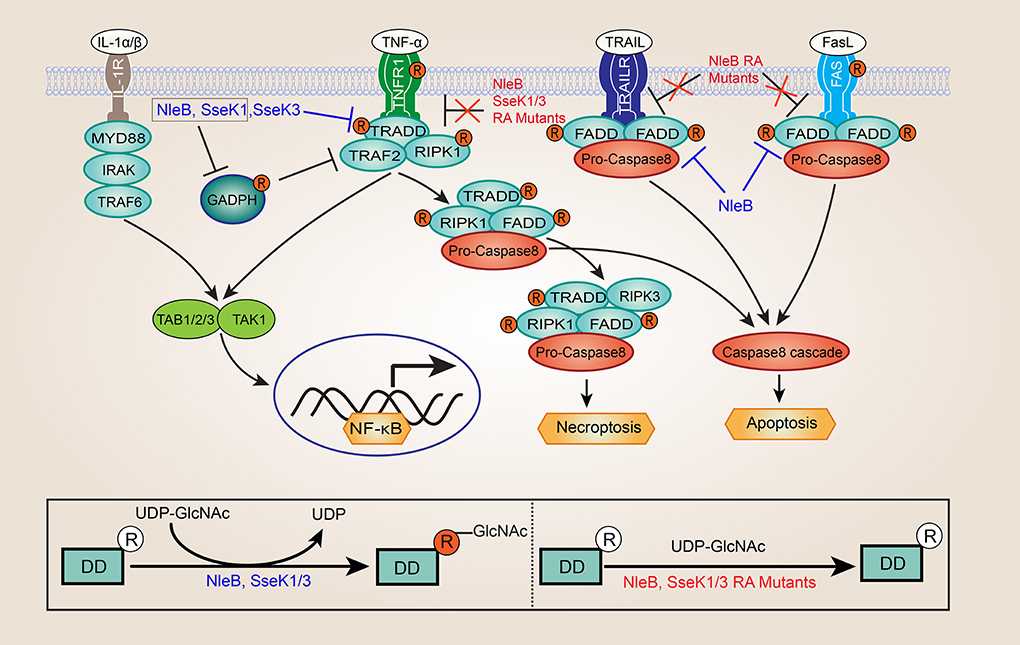


Frontiers Bacteria Catalyzed Arginine Glycosylation In Pathogens And Host Cellular And Infection Microbiology



Arginine Wikiwand



Arginine Derivatives Suitable For Side Chain Derivatization



Arginine Enveloped Virus Inactivation And Potential Mechanisms Meingast Biotechnology Progress Wiley Online Library
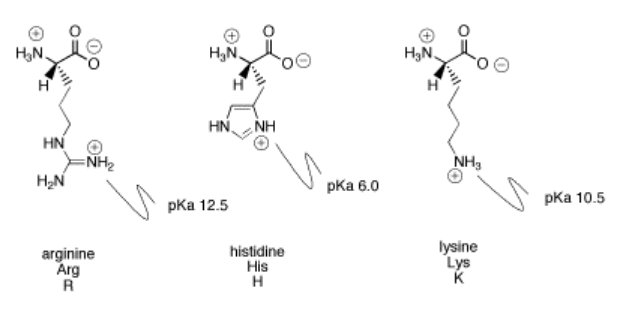


Arginine Pka


Chem 245 Amino Acids


More Biologically Active Amines
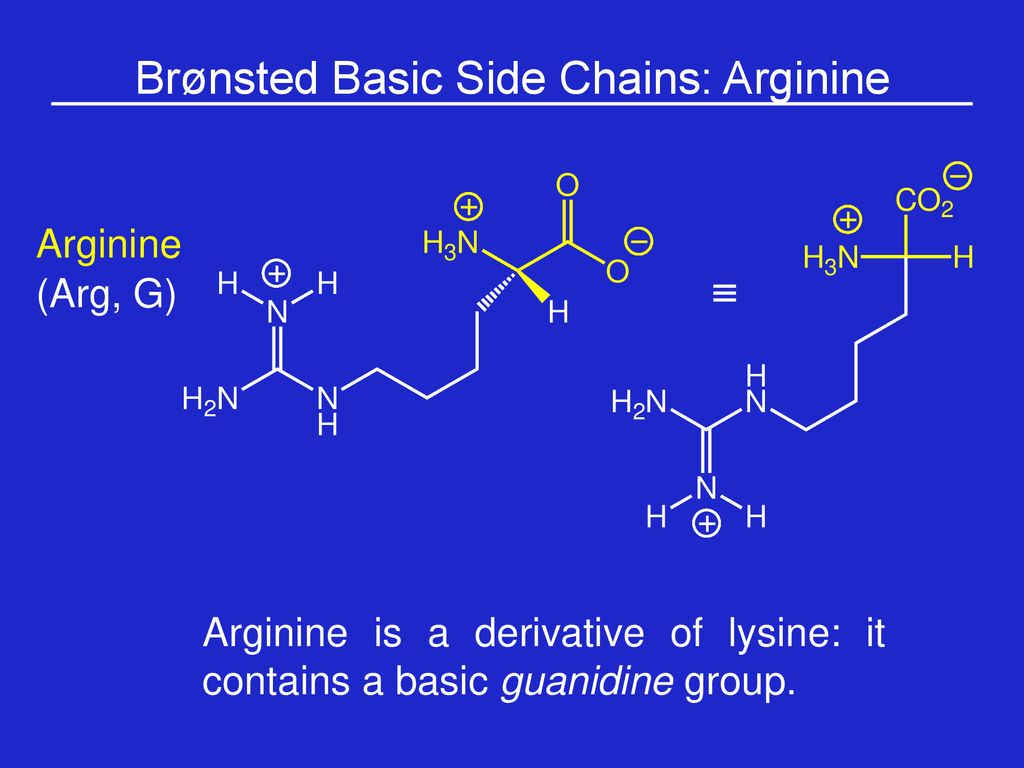


Week 1 Amino Acids Prof Sbw Ppt Download


Study Of The Affinity Between The Protein Kinase Pka And Peptide Substrates Derived From Kemptide Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations And Mm Gbsa



Selective Labelling Of Arginine Residues Engaged In Binding Sulfatedglycosaminoglycans Biorxiv



Ds 1 Pdf Discussion Guide Week 1 Ph Pka And Buffering Model Exam Question Hendersson Hasselbach Equation Ph Pka Log A Ha Ph Is A Log Scale So Course Hero
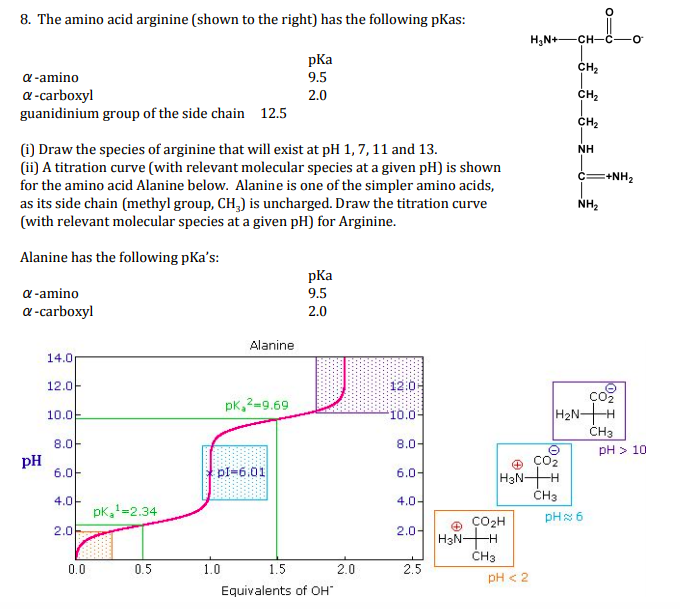


Solved 8 The Amino Acid Arginine Shown To The Right Ha Chegg Com
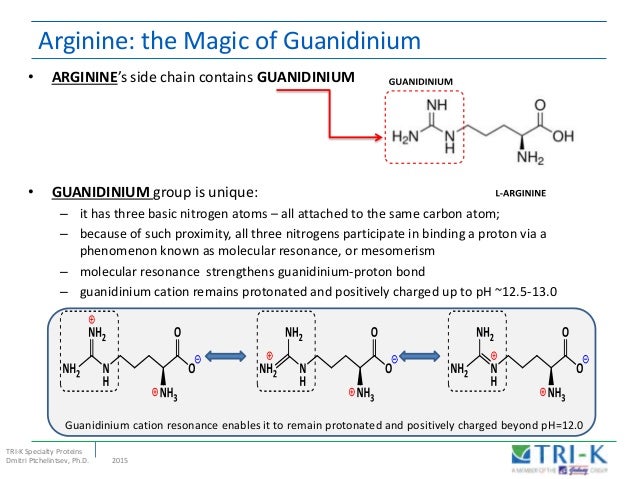


Brain Mind Article Arginine Side Chain Charge


Amino Acids Arginine R Arg
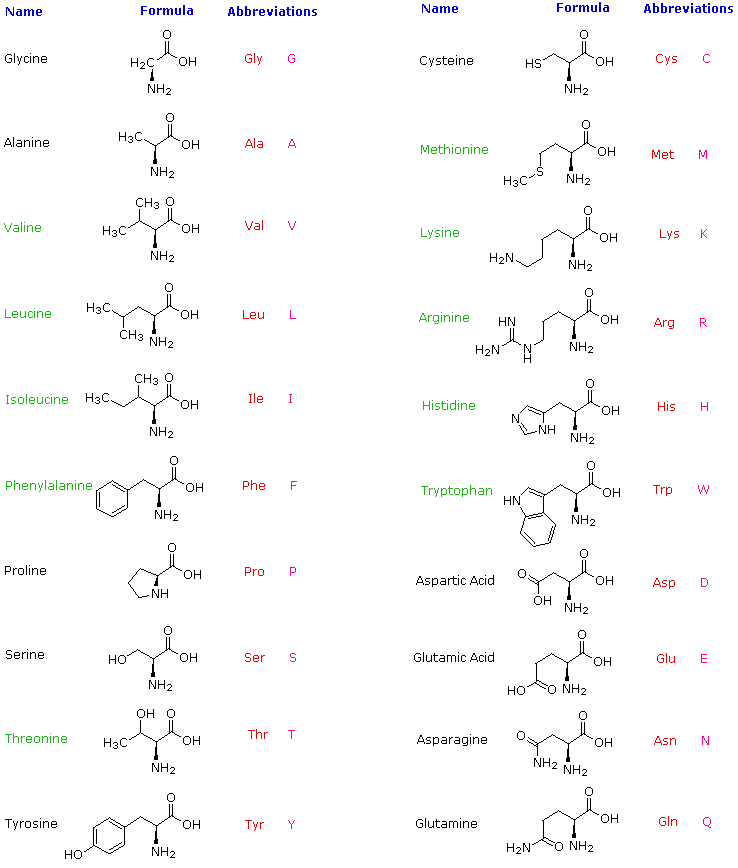


Proteins



Arginine Derivatives Suitable For Side Chain Derivatization



Exceptionally Versatile Arginine In Bacterial Post Translational Protein Modifications



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿